This post describes my setup for writing RTL and viewing synthesis output in real-time. It’s essentially a poor man’s IDE that uses multiple VS Code windows and automatically reruns commands on file save.
This is also a good opportunity to explore the Yosys synthesis flow and commands in detail. Let’s start with my go-to Makefile for experimenting with Yosys:
all:
yosys synth.ys
netlistsvg top.vis.json -o top.vis.svg
convert top.vis.svg top.vis.png
netlistsvg top.synth.json -o top.synth.svg
convert top.synth.svg top.synth.png
netlistsvg top.pdk.json -o top.pdk.svg
convert top.pdk.svg top.pdk.png
Yosys Script Link to heading
The first step is reading the Verilog code using read_verilog. For simplicity, this setup uses a single file called top.v.
read_verilog -sv top.v
Prep Link to heading
The next stage runs prep, which executes three key passes:
- proc — converts always blocks into lower-level logic.
- flatten — inlines instantiated submodules.
- opt — performs basic optimizations like removing unused wires.
prep -top top
write_json top.vis.json
write_verilog top.vis.v
show -format png -prefix top.vis.yosys
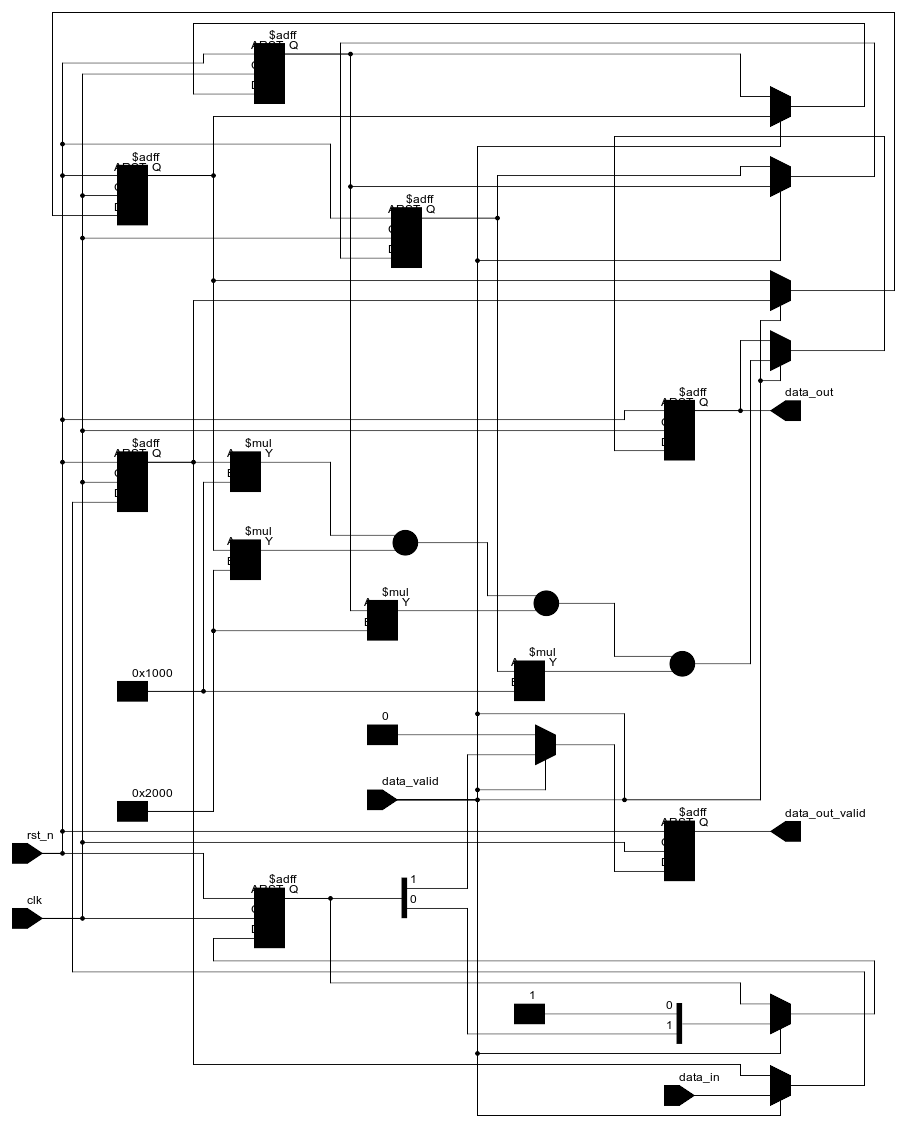
This stage generates two PNG diagrams. The first, top.vis.yosys.png, is created by Yosys using Graphviz via the show -format png -prefix top.vis.yosys command.
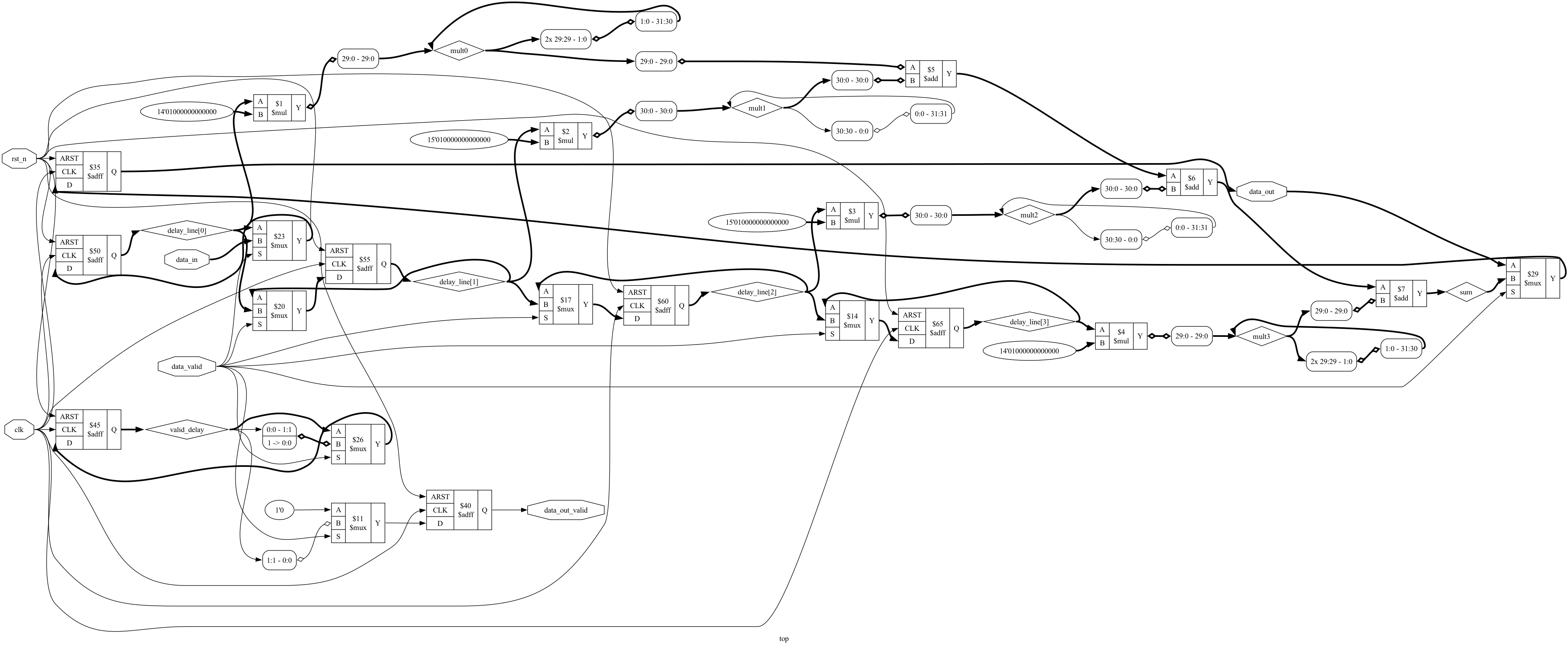
The second diagram provides a cleaner visualization by piping the JSON output through netlistsvg and converting the resulting SVG to PNG.
At the end of prep, we can print Yosys stats as follows:
2.12. Printing statistics.
=== top ===
Number of wires: 50
Number of wire bits: 92
Number of public wires: 11
Number of public wire bits: 33
Number of ports: 4
Number of port bits: 7
Number of memories: 0
Number of memory bits: 0
Number of processes: 0
Number of cells: 47
$add 2
$adff 8
$eq 23
$logic_not 3
$mux 3
$not 1
$pmux 4
$reduce_or 3
Synth Link to heading
Next, we generate a generic netlist from the RTL. The synth command orchestrates this process through several passes:
- Invokes
proc,opt, andmemorypasses. - Performs logic optimization.
- Converts high-level constructs (processes, memories, FSMs) into gate-level logic.
synth -top top
write_json top.synth.json
write_verilog top.synth.v
write_blif top.synth.blif
write_edif top.synth.edif
show -format png -prefix top.synth.yosys
At this stage, we generate 2 diagrams of the netlist (one from Yosys and one from netlistsvg).

Finally, we can see the synthesis report with technology-independent cells.
6.25. Printing statistics.
=== top ===
Number of wires: 120
Number of wire bits: 178
Number of public wires: 11
Number of public wire bits: 33
Number of ports: 4
Number of port bits: 7
Number of memories: 0
Number of memory bits: 0
Number of processes: 0
Number of cells: 146
$_ANDNOT_ 32
$_AND_ 8
$_DFFE_PN0N_ 1
$_DFF_PN0_ 22
$_MUX_ 3
$_NAND_ 15
$_NOR_ 3
$_NOT_ 4
$_ORNOT_ 8
$_OR_ 38
$_XNOR_ 2
$_XOR_ 10
dfflibmap and abc Link to heading
The final step maps generic cells to a specific technology library. I typically use NangateOpenCellLibrary_typical.lib. However, diagrams aren’t particularly useful at this stage for two reasons:
- The netlist becomes difficult to trace due to the proliferation of cells and wires after technology mapping.
netlistsvgcannot process the netlist at this level of detail.
dfflibmap handles the mapping of flip-flops, while abc performs combinational logic mapping:
dfflibmap -prepare -liberty NangateOpenCellLibrary_typical.lib
abc -liberty NangateOpenCellLibrary_typical.lib
dfflibmap -liberty NangateOpenCellLibrary_typical.lib
write_json top.pdk.json
write_verilog top.pdk.v
write_blif top.pdk.blif
write_edif top.pdk.edif
show -format png -prefix top.pdk.yosys
stat
As always, looking at the stats:
1. Printing statistics.
=== top ===
Number of wires: 225
Number of wire bits: 283
Number of public wires: 11
Number of public wire bits: 33
Number of ports: 4
Number of port bits: 7
Number of memories: 0
Number of memory bits: 0
Number of processes: 0
Number of cells: 77
AND2_X1 3
AND4_X1 1
AOI21_X1 6
AOI221_X1 2
AOI222_X1 2
AOI22_X1 4
DFFR_X1 23
INV_X1 7
MUX2_X1 1
NAND2_X1 4
NAND3_X1 3
NAND4_X1 2
NOR2_X1 5
OR2_X1 1
XNOR2_X1 9
XOR2_X1 4
Bonus: Build on Save Link to heading
The Build on Save VS Code extension triggers a build automatically whenever the file is saved. Here’s a sample .vscode/settings.json configuration:
{
"emeraldwalk.runonsave": {
"commands": [
{
"match": "top.v",
"cmd": "make"
}
]
}
}
Bonus: OpenSTA Link to heading
Running static timing analysis with OpenSTA provides valuable feedback on timing violations and negative slack. First, create a simple SDC constraints file named constraints.sdc.
# Define the clock
create_clock -name CLK -period 10 [get_ports clk]
Then add the STA command to the all target in the Makefile:
sta run_sta.tcl
read_verilog top.synth.v
read_liberty NangateOpenCellLibrary_typical.lib
link_design top
read_sdc constraints.sdc
report_checks
report_tns
report_wns
report_checks -path_delay min -format full > sta.setup_report.rpt
report_checks -path_delay max -format full > sta.hold_report.rpt
With this command in the Makefile, STA will automatically run whenever you save the file.
Delay Time Description
---------------------------------------------------------
0.00 0.00 clock CLK (rise edge)
0.00 0.00 clock network delay (ideal)
0.00 0.00 ^ _1247_/CK (DFFR_X1)
0.11 0.11 ^ _1247_/Q (DFFR_X1)
0.06 0.17 ^ _0914_/Z (XOR2_X1)
0.03 0.20 v _0915_/ZN (XNOR2_X1)
0.06 0.26 v _0917_/Z (XOR2_X1)
0.06 0.32 v _0918_/Z (XOR2_X1)
0.06 0.38 ^ _0921_/ZN (NOR3_X1)
0.03 0.41 v _0926_/ZN (OAI21_X1)
0.06 0.47 ^ _0966_/ZN (AOI211_X1)
0.04 0.51 v _0971_/ZN (OAI33_X1)
0.05 0.56 ^ _0984_/ZN (AOI21_X1)
0.03 0.59 v _0999_/ZN (OAI21_X1)
0.04 0.63 ^ _1013_/ZN (AOI21_X1)
0.03 0.66 v _1030_/ZN (OAI21_X1)
0.05 0.71 ^ _1043_/ZN (AOI21_X1)
0.03 0.75 v _1084_/ZN (OAI211_X1)
0.05 0.79 v _1085_/ZN (AND3_X1)
0.10 0.89 ^ _1121_/ZN (OAI33_X1)
0.03 0.93 v _1124_/ZN (OAI21_X1)
0.04 0.97 v _1130_/ZN (XNOR2_X1)
0.06 1.03 v _1131_/Z (MUX2_X1)
0.00 1.03 v _1224_/D (DFFR_X1)
1.03 data arrival time
1.00 1.00 clock CLK (rise edge)
0.00 1.00 clock network delay (ideal)
0.00 1.00 clock reconvergence pessimism
1.00 ^ _1224_/CK (DFFR_X1)
-0.04 0.96 library setup time
0.96 data required time
---------------------------------------------------------
0.96 data required time
-1.03 data arrival time
---------------------------------------------------------
-0.07 slack (VIOLATED)
tns max -0.15
wns max -0.07