In previous post, I wrote simple Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm, so I wanted to do elliptical curve key exchange as well. Again, The math is there in crypto book. but the algorithm is simple(strangely simple).
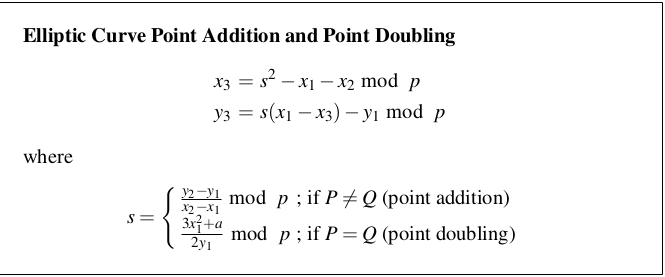
The trick is calculating aP where P is point on the elliptical curve that satisfies y^2 = x^3+ a.x + y. The following algorithm calculates the addition (and incase 2 points are the same, it is doubling).
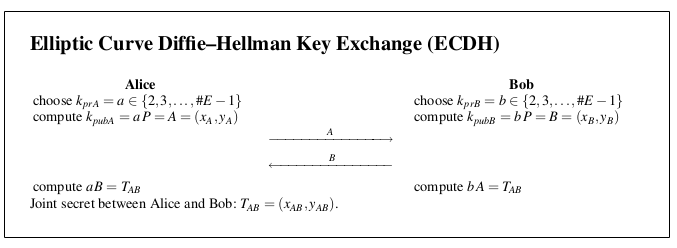
In the code below, A and B share public keys(should be random integers) and the both side calculate the key with using their own private key and key shared form other side.
A public key:(10,6)
B public key:(7,11)
A key: (13,10)
B key: (13,10)
The whole thing
class EC():
def __init__(self, x, y, a ,p):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.a = a
self.p = p
def mult(self, m):
assert( m >= 2 )
def add(x1, y1, x2, y2, a, p):
if x1 == x2 and y1 == y2:
s = ((3 * x1 * x1) + a) * pow(2 * y1, -1, p) % p
else:
s = (y2-y1)* pow(x2-x1,-1,p) % p
x3 = pow( (s*s) - x1 - x2 , 1, p)
y3 = pow( (s *(x1 - x3)) - y1 , 1, p)
return (x3,y3)
(x3,y3) = add(self.x, self.y,self.x, self.y, self.a, self.p)
for i in range(m-2):
(x3,y3) = add(self.x, self.y, x3, y3, self.a, self.p)
r = EC(x3, y3, self.a, self.p)
return r
def __str__(self):
return f'({self.x},{self.y})'
p = 17
a = 2
b = 2
P = EC(5,1, a, p)
kpr_A = 3
kpub_A = P.mult(kpr_A)
print(f'A public key:{kpub_A}')
kpr_B = 10
kpub_B = P.mult(kpr_B)
print(f'B public key:{kpub_B}')
TabA = kpub_B.mult(kpr_A)
print(f'A key: {TabA}')
TabB = kpub_A.mult(kpr_B)
print(f'B key: {TabB}')